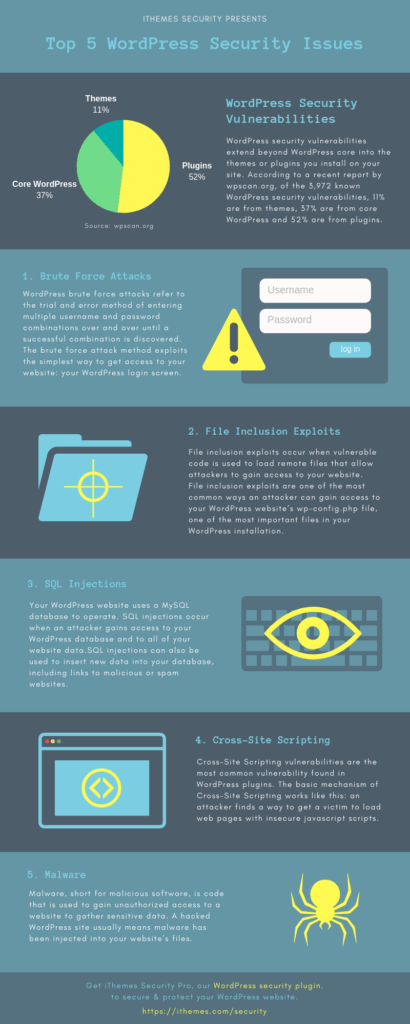
WordPress security vulnerabilities extend beyond WordPress core into the themes or plugins you install on your site.
According to a recent report by wpscan.org, of the 3,972 known WordPress security vulnerabilities, 11% are from themes, 37% are from core WordPress and 52% are from plugins.
1. Brute Force Attacks
WordPress brute force attacks refer to the trial and error method of entering multiple username and password combinations over and over until a successful combination is discovered. The brute force attack method exploits the simplest way to get access to your website: your WordPress login screen.
2. File Inclusion Exploits
File inclusion exploits occur when vulnerable code is used to load remote files that allow attackers to gain access to your website. File inclusion exploits are one of the most common ways an attacker can gain access to your WordPress website’s wp-config.php file, one of the most important files in your WordPress installation.
3. SQL Injections
Your WordPress website uses a MySQL database to operate. SQL injections occur when an attacker gains access to your WordPress database and to all of your website data.SQL injections can also be used to insert new data into your database, including links to malicious or spam websites.
4. Cross-Site Scripting
Cross-Site Scripting vulnerabilities are the most common vulnerability found in WordPress plugins. The basic mechanism of Cross-Site Scripting works like this: an attacker finds a way to get a victim to load web pages with insecure javascript scripts.
5. Malware
Malware, short for malicious software, is code that is used to gain unauthorized access to a website to gather sensitive data. A hacked WordPress site usually means malware has been injected into your website’s files.
Get iThemes SecurityPro, our WordPress security plugin, to secure & protect yourWordPress website. https://ithemes.com/security


